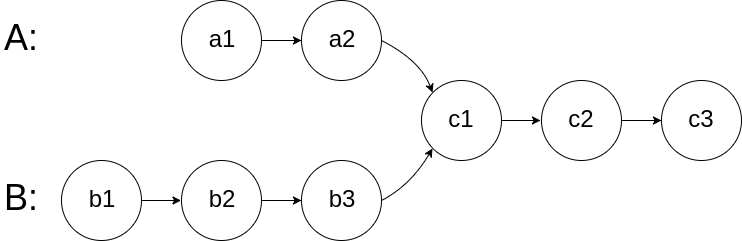
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
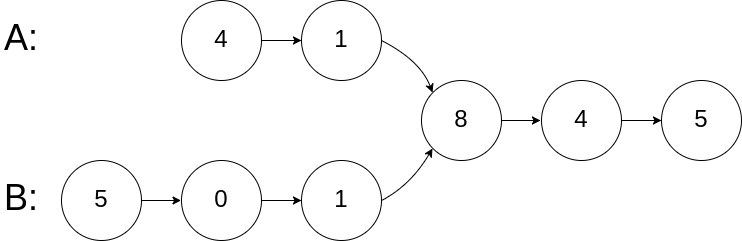
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5],
skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be
0 if the two lists intersect).
From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as
[5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3
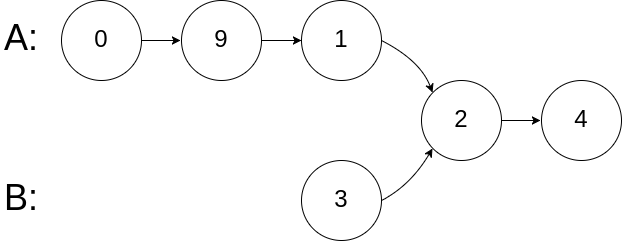
nodes before the intersected node in B.Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not
be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4].
From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected
node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.解题要点:
Last updated